Appendix G. Optimizing Injection Strategies and In situ Remediation Performance
Click here to view the entire Appendix G in Adobe PDF format.
The links below will open individual survey questions.
Q1
Identify your affiliation
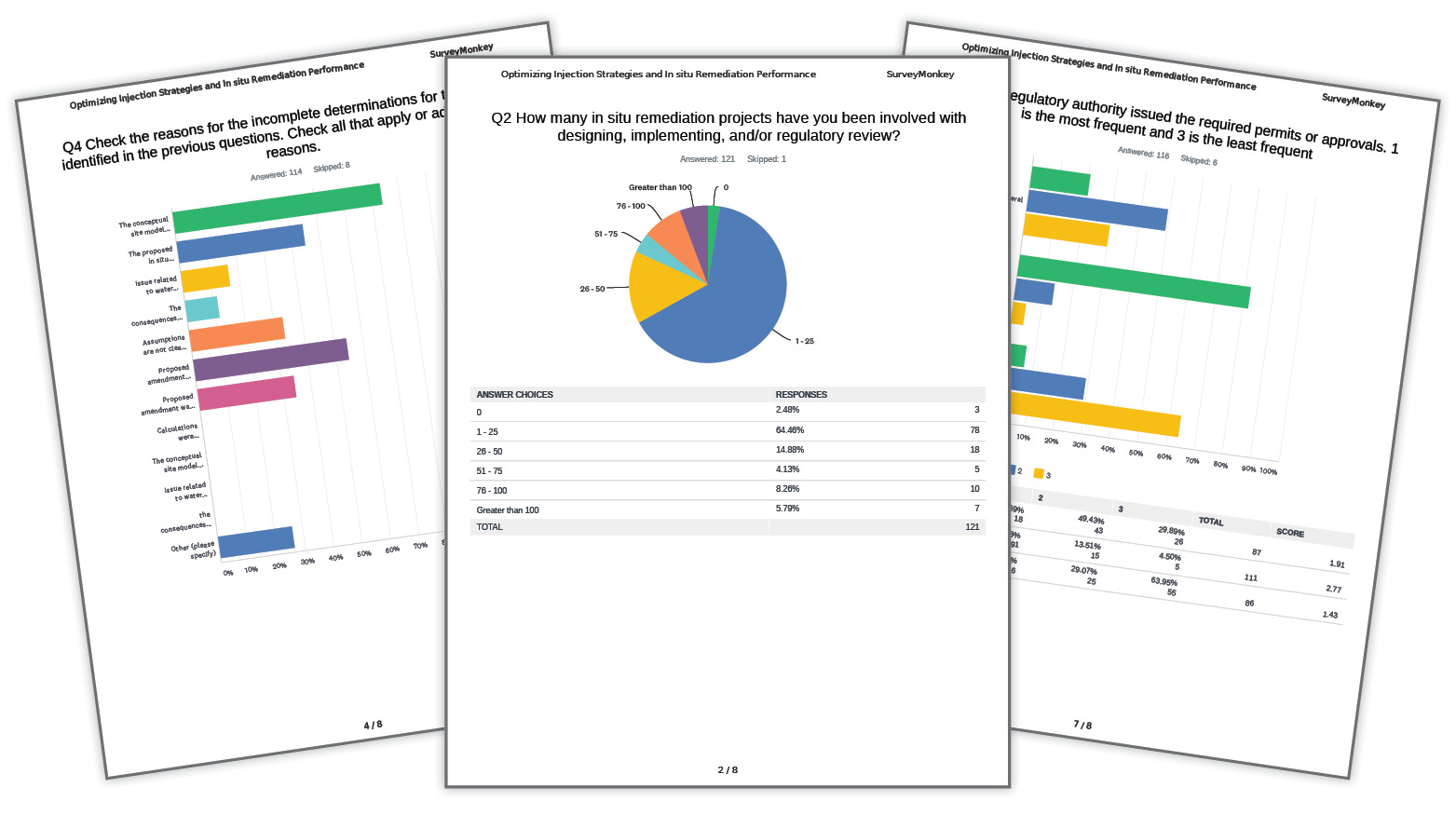
Q2
How many in situ remediation projects have you been involved with designing, implementing, and/or regulatory review?
Q3
From the number of projects identified in the previous question; what percentage of projects did not provide adequate information in the first submittal to demonstrate the selected remedy would be successful?
Q4
Check the reasons for the incomplete determinations for the projects identified in the previous questions. Check all that apply or add additional reasons.
Q5
What was the root cause(s) for the inadequate information provided in those projects that did not support the selected remedy?
Q6
Which regulatory authority issued the required permits or approvals. 1 is the most frequent and 3 is the least frequent
Q7
Please include your contact information in case clarification is required
Click here to download the entire document.


